
Bhubaneswar: The birth place of hMPV is not China. This respiratory virus was first identified in the Netherlands 24 years back – in year 2001.
However, serologic (blood serum) studies of antibodies against HMPV indicate that the virus is not new and circulated in humans for at least 50 years, suggest US CDC data.
hMPV GLOBAL BURDEN
In 2018, it was estimated that around 11.1 million cases of acute lower respiratory infections globally were attributable to HMPV, leading to approximately 502,000 hospitalizations and 113,000 fatalities, shows the US, CDC data.
CHINA’S TRYST WITH hMPV
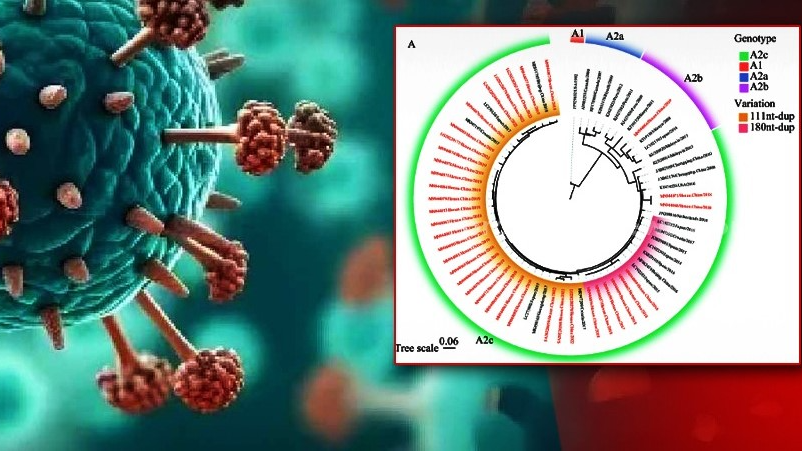
The virus was in circulation in China since 2005.
It was place: Changsha. And year was 2007-2008.
The prevalence and clinical characteristics of hMPV were determined in nasopharyngeal swabs of children.
A RT-PCR employed to screen for both hMPV and other common respiratory viruses in 1,165 nasopharyngeal swabs taken from children with lower respiratory tract infections.
Seventy-six of 1,165 (6.5%) specimens were positive for hMPV, of which 85.5% occurred in the winter and spring seasons.
CHINA CDC 2024 STUDY ON hMPV
hMPV outbreak in China in 2024-25 is not a new outbreak. Records with China Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) shows controlled outbreaks in one or two provinces since 2007.
In the United States, the early 2023 detection rates for HMPV rose from 7% to between 10% and 19%
China has recorded two big outbreaks in 2018 and 2019, suggest the CDC data.
Henan, a populous province in China, has maintained ongoing surveillance for influenza-like illness (ILI) since 2010 and severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) since 2015.
Following consistent outbreaks leading to mortalities, the CDC has conducted an exhaustive study on hMPV taking the specimens collected from 2,707 ARI patients from a longer period from October 2017 to March 2023. The age of participants ranged from 5 months to 17 years.
The study has the following details.
HOW TO KNOW hMPV?
As per the CDC, China study, the prevalence of HMPV was higher in patients with ILIs compared to those with SARIs.
WHAT IS INFLUENZA LIKE ILLNESS?
As per medical classification, ILI cases were defined as –
WHAT IS SEVERE ACUTE RESPIRATORY INFECTION?
A case is described as Severe Acute Respiratory Infection (SARI) with ---
PREDOMINANT SYMPTOMS
IN HOW MANY DAYS hMPV GETS SEVERE?
As per studies in Journal of Medical Biology, study on mice shows, initially HMPV infection in the lung is characterized by inflammation with alveola lining cells from day 3 with a peak on day 5.
The inflammation of inner lining of lungs alvela (air sacc) will make the patient harder to breathe.
The study shows the inflammation subsides after five days, only to return with bang after 2-3 weeks, to develop in a more prominent peribronchiolar and perivascular infiltrate – leading to airway obstruction in mice.
The mice hMPV study shows such conditions in lungs continuing for 70 long days, indicating long-term pulmonary inflammation after HMPV infection.
WHO ARE CARRIERS OR SPREADERS?
Though in young children, HMPV is the second most common cause of lower Respiratory tract infection after RSV, with children less than one year of age showing the highest rates of infection]. Seroprevalence (means antibody generated) at the age of 5 is almost 100%
WHEN TO SEE DOCTOR?
Immediately, report to a good doctor, if you have the following conditions.
TREATMENT FOR MILD CASES
Though no treatment or vaccine is specified for hMPV, the treatment in mild cases is akin to treatment for cold and cough.