376 High Court Judge vacancies, says Union Law Minister Meghwal

Rijiju defends 'JPC Report on Waqf Bill', says dissent notes Included, rejects opposition claims of unconstitutionality
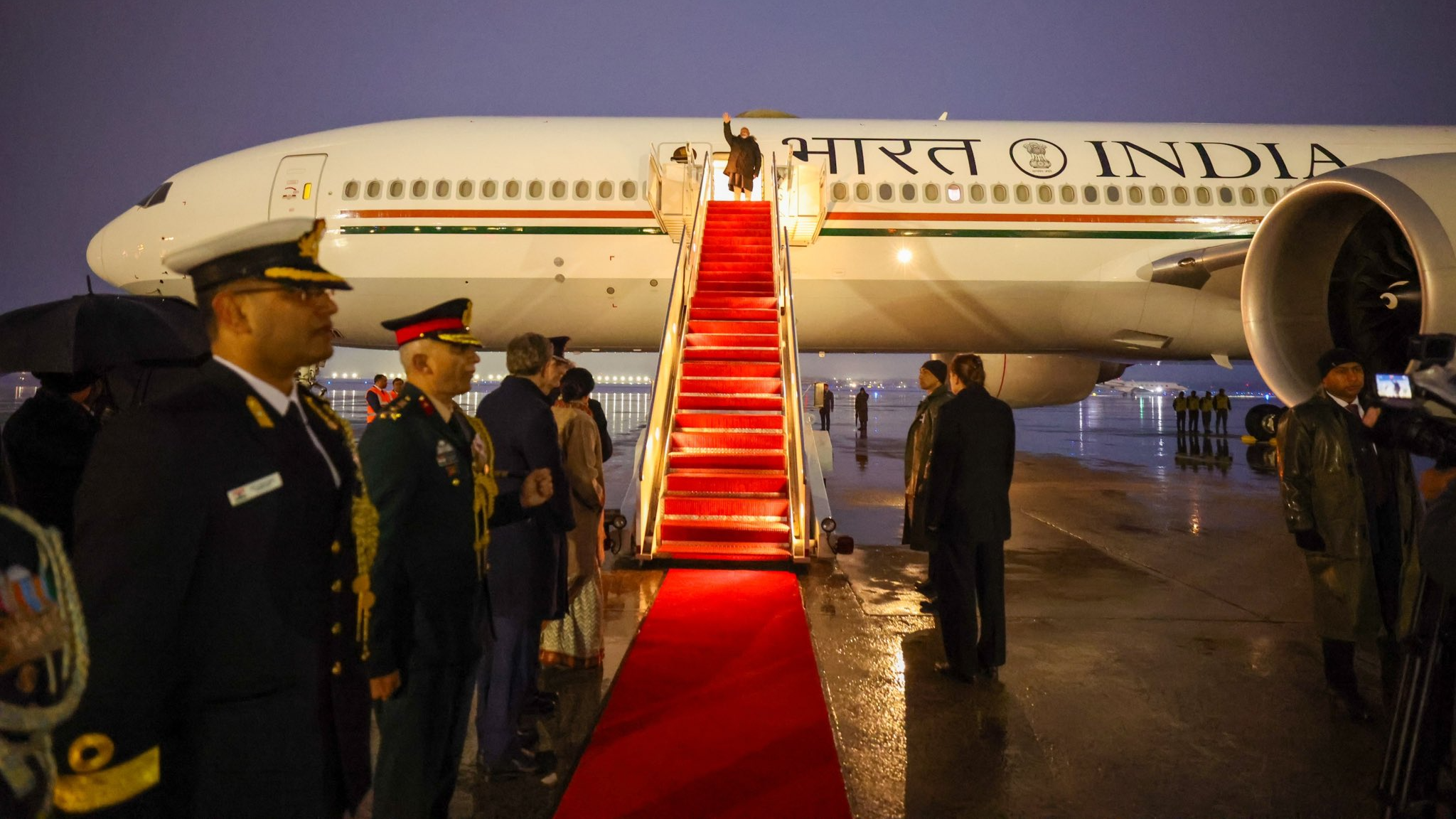

PM Narendra Modi arrives in US capital Washington DC, meets Intel Chief Tulsi Gabbard

Samay Raina deletes 'India's Got Latent' Episodes, pledges cooperation with Agencies

Ahmedabad Rout: India reigns 3-0 Series Victory Over England in Ahmedabad

Supreme Court Slams ‘Election Freebies Culture’, Says ‘People Losing Will to Work’
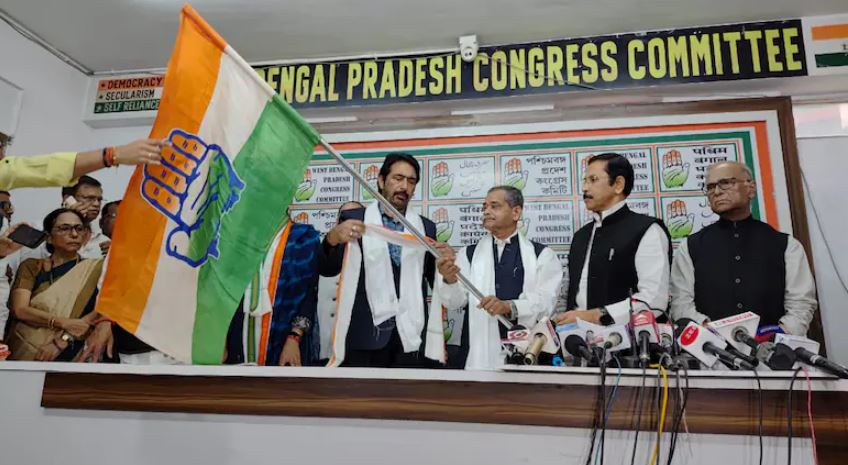

Pranab Mukherjee’s son rejoins Congress after brief stint with TMC

1984 Anti-Sikh Riots: Ex-Congress MP Sajjan Kumar convicted in Delhi murder case

Atul Subhash re-run: Odia rapper ‘Juggernaut’ commits suicide in Bengaluru, family accuses wife of harassment
Husband’s forced, unnatural sex with wife not crime, rules Chhattisgarh HC; stokes marital rape law debate! EXCLUSIVE
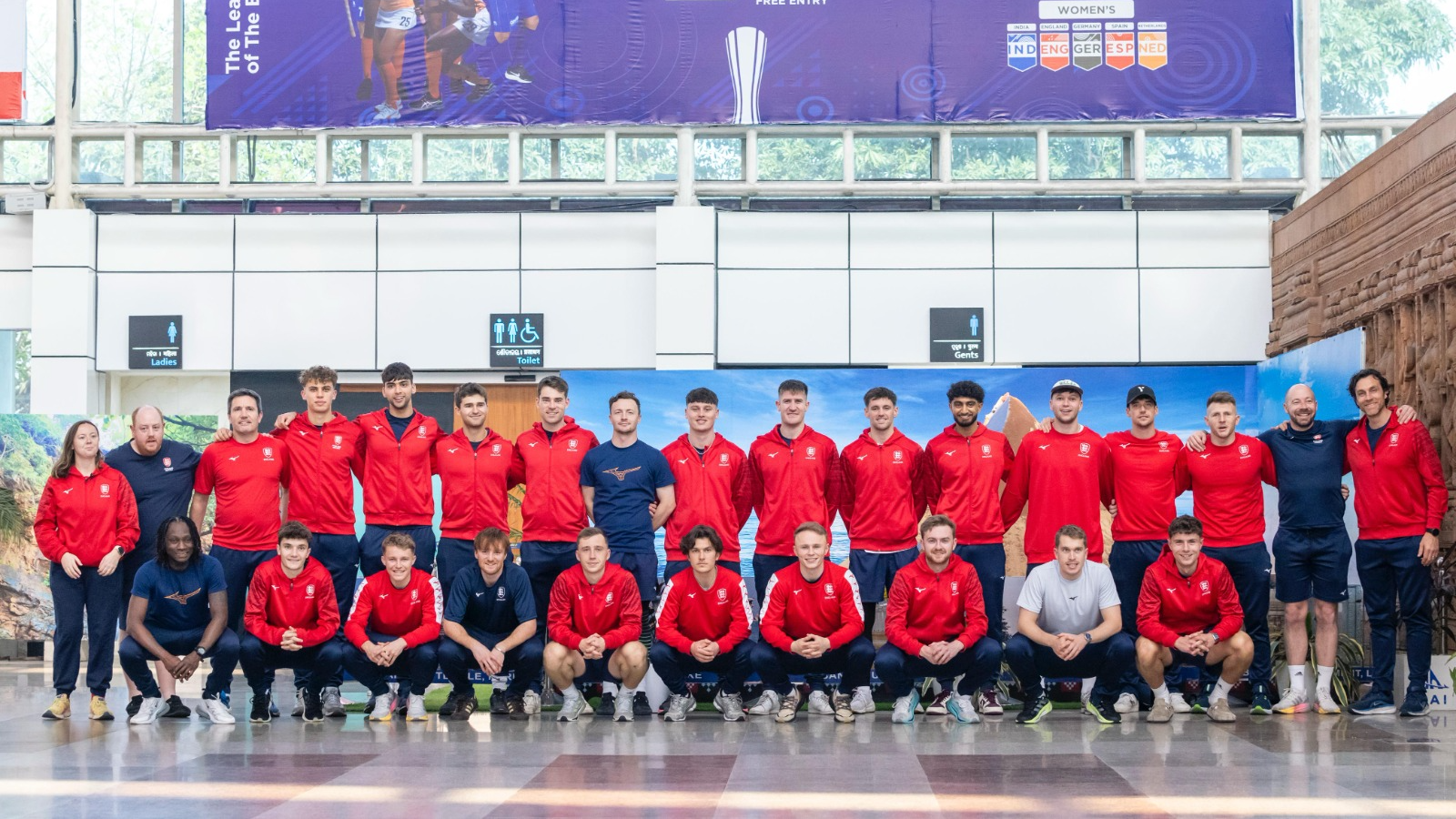

Upbeat England Men’s Hockey Team arrives in Bhubaneswar for FIH Pro League 2024-25

India's PM Modi Fourth Foreign Leader to Meet Trump in Unprecedented Diplomatic Sprint: Inching Closer to White House
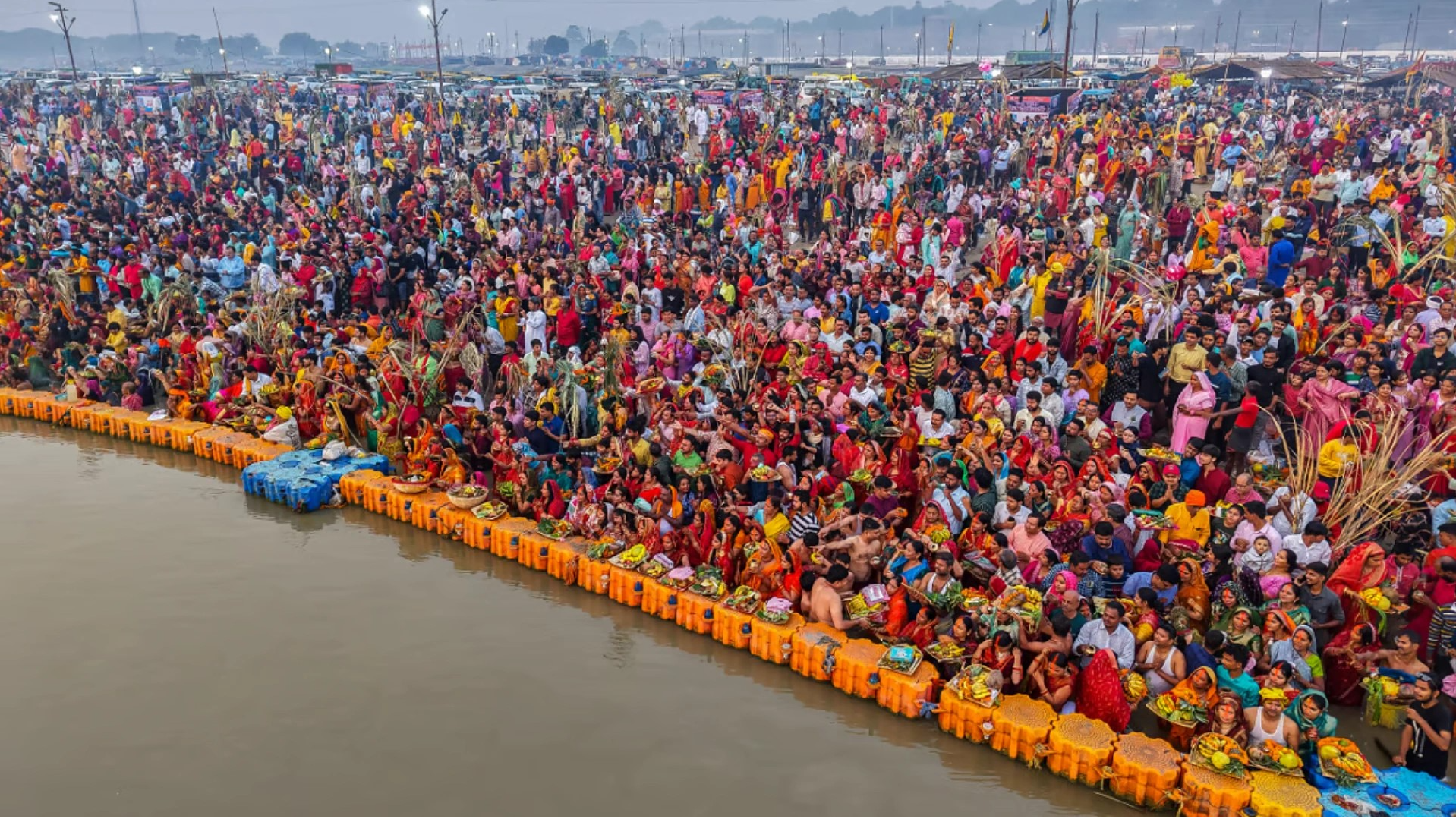

Maha Kumbh Mela 2025: Lakhs of devotees throng Triveni Sangam on occasion of 'Maghi Purnima'

Ram Janmabhoomi Temple's Chief Priest and Spiritual Guardian, Acharya Satyendra Das, Dies After Brain Stroke: 5 lesser known facts about him

Supreme Court directs ECI to preserve EVM data during verification

Two soldiers killed in suspected IED blast in Jammu & Kashmir’s Akhnoor Sector
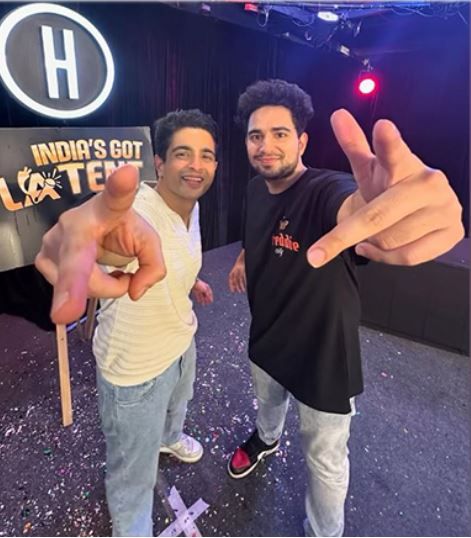

NCW summons Ranveer Allahbadia for hearing on February 17 over vulgar remarks

Kapil Sibal calls for clear government vision on AI and strategy for US tariff dispute

Government Intervenes: Controversial 'India's Got Latent' featuring Ranveer Allahbadia Episode Removed from YouTube in India